|
|||||||||||||

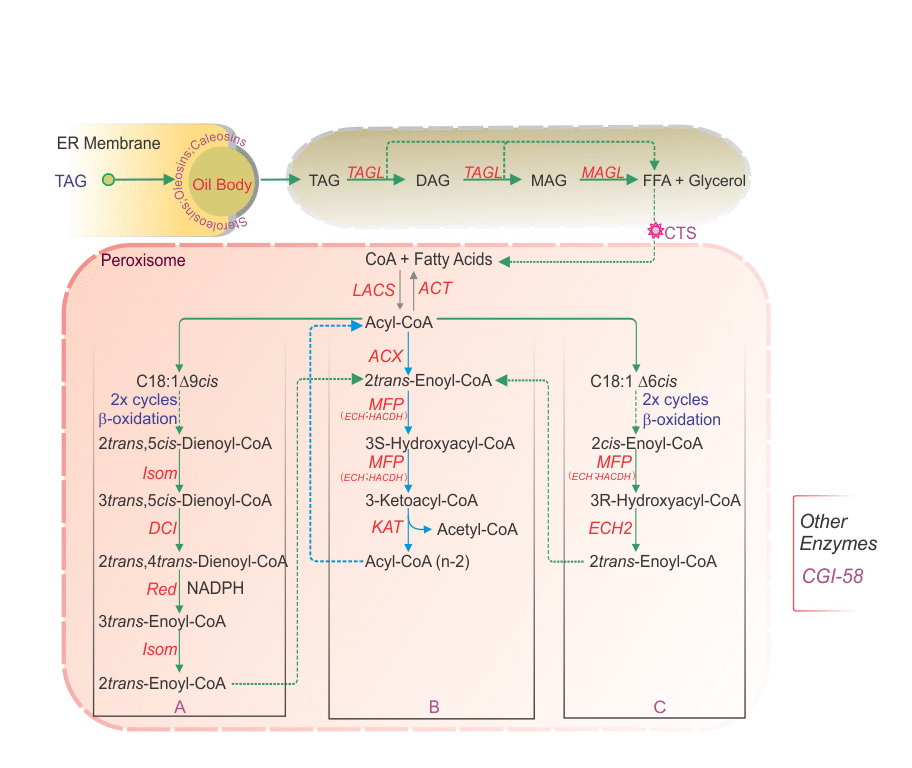
Legend: (A) Examples of the involvement of auxiliary activities in the degradation of oleic acid (C18:1Δ9cis). (B) The core b-oxidation cycle. (C) Example of the involvement of the monofunctional type 2 enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH2) in the degradation of fatty acids with a cis double bond on an even-numbered carbon (C18:1Δ6cis, petroselinic acid). Triacylglycerols are first degraded by cellular lipases to relases free fatty acids from glycerol. Then reactions involved in the β-oxidation of straight chain fatty acids in the peroxisome (adopted from Goepfert and Poirier 2007). â2x cyclesâ indicates that the molecule undergoes two successive rounds through the β-oxidation cycle. CTS is an ABC transporter involved in the import of β-oxidation substrates to the peroxisome.
Abbreviations: ACT, acyl-CoA thioesterase; ACX, acyl-CoA oxidase; DCI1, D3,5,D2,4-dienoyl-CoA isomerase; Isom, D3,D2-enoyl-CoA isomerase; KAT, 3-ketothiolase; LACS, long chain acyl-CoA synthetase; MFP, multifunctional protein containing a 2trans-enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECH) and a 3S-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HACDH); Red, 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase; TAGL, triacylglycerol lipase; MFP represents only the 2E-enoyl-CoA hydratase activity of the multifunctional protein.
Contributors:
Ian Graham
Fatty Acid β-Oxidation
, Vincent Arondel, and Rémi ZALLOT
Triacylglycerol Lipases
Triacylglycerol & Fatty Acid Degradation
|
|||||||||||||
-
Home &
Pathways- Home
- Fatty Acid Synth
- Plast FAE & Desat
- Prok Gal/Sulpho I
- Prok Gal/Sulpho II
- Euk Gal/Sulpho
- TAG Synthesis
- Euk Phospholipid
- TAG Degradation
- FA Elong & Wax
- Sphingolipid I
- Sphingolipid II
- Mito FAS & Lipoic
- Mito LipoPolSach
- Mito Phospholipid
- Trafficking
- Cutin I
- Cutin II
- Suberin I
- Suberin II
- Suberin III
- Oxylipin I
- Oxylipin II
- Signaling
-
Enzyme/Protein
Summary -
Loci
Summary -
Structures &
Schemas -
Lipid methods
& composition - Mutants
- Downloads
- About
- Comments


