|
|||||||||||||

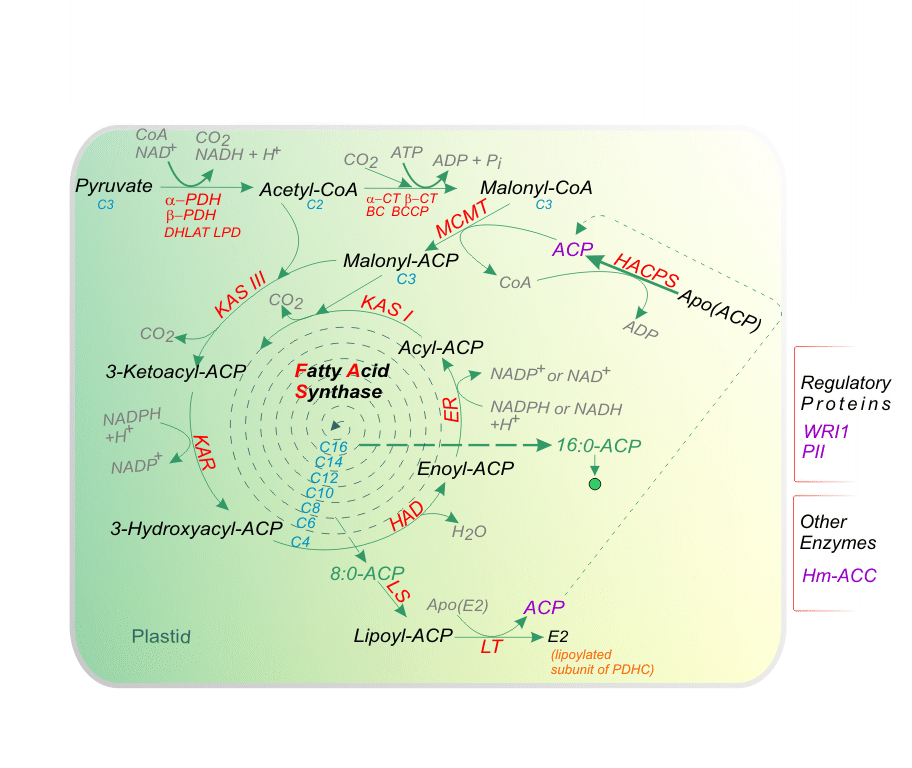
Legend: The plastidial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex generates acetyl-coenzyme A that is used as a building block for fatty acid production. Fatty acids are grown by sequential condensation of two-carbon units by enzymes of the fatty acid synthase complex. During each cycle four reactions occur: condensation, reduction, dehydration and reduction. Acyl carrier protein is a cofactor in all reactions. Synthesis of a C16 fatty acid requires that the cycle be repeated seven times. During the first turn of the cycle, the condensation reaction is catalyzed by ketoacyl-ACP synthase (KAS) III. For the next six turns of the cycle, the condensation reaction is catalyzed by isoform I of KAS. Finally, KAS II is used during the conversion of 16:0 to 18:0.
Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACP, acyl carrier protein; BC, biotin carboxylase; BCCP, biotin carboxyl carrier protein; CT, carboxyltransferase; DHLAT, dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase; ER, enoyl-ACP reductase; HACPS, holo-ACP synthase; HAD, hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydrase; KAR, ketoacyl-ACP reductase; KAS, ketoacyl-ACP synthase; LPD, dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase; LS, lipoate synthase; LT, lipoyltransferase; MCMT, malonyl-CoA: ACP malonyltransferase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDHC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Fatty Acid Synthesis
|
|||||||||||||
-
Home &
Pathways- Home
- Fatty Acid Synth
- Plast FAE & Desat
- Prok Gal/Sulpho I
- Prok Gal/Sulpho II
- Euk Gal/Sulpho
- TAG Synthesis
- Euk Phospholipid
- TAG Degradation
- FA Elong & Wax
- Sphingolipid I
- Sphingolipid II
- Mito FAS & Lipoic
- Mito LipoPolSach
- Mito Phospholipid
- Trafficking
- Cutin I
- Cutin II
- Suberin I
- Suberin II
- Suberin III
- Oxylipin I
- Oxylipin II
- Signaling
-
Enzyme/Protein
Summary -
Loci
Summary -
Structures &
Schemas -
Lipid methods
& composition - Mutants
- Downloads
- About
- Comments


