|
|||||||||||||

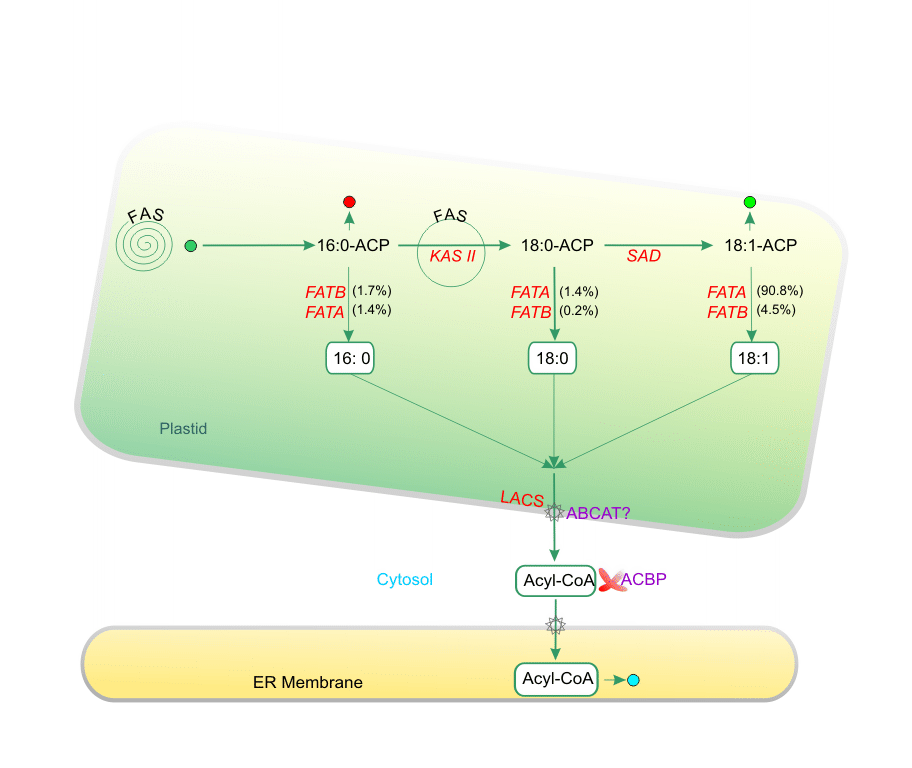
Legend: C16:0 fatty acids produced by the pathways shown in Figure 1A can enter three possible reactions. First, they can be elongated by an additional cycle of fatty acid synthesis. In these cases, KAS II is used during the conversion of 16:0 to 18:0. Alternatively, C16:0 can enter prokaryotic glycerolipid pathway as shown in Figure 2. Finally, 16:0-ACP can be hydrolyzed by FATB thioesterase to release free fatty acids that are exported from the plastid. Most 18:0-ACP produced by elongation is desaturated by the stearoyl-ACP desaturase. The resulting 18:1-ACP can either enter the prokaryotic glycerolipid pathway (Figure 2), or be hydrolyzed by FATA for export from the plastid.
Abbreviations: Abbreviations: ABCAT, ABC acyl transporter; ACBP, acyl-CoA binding protein; ACP, acyl carrier protein; FAS, fatty acid synthase; FATA (B), fatty acyl thioesterase A (B); KAS, ketoacyl-ACP synthase; LACS, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; SAD, stearoyl-ACP desaturase. Fatty Acid Elongation, Desaturation & Export From Plastid
|
|||||||||||||
-
Home &
Pathways- Home
- Fatty Acid Synth
- Plast FAE & Desat
- Prok Gal/Sulpho I
- Prok Gal/Sulpho II
- Euk Gal/Sulpho
- TAG Synthesis
- Euk Phospholipid
- TAG Degradation
- FA Elong & Wax
- Sphingolipid I
- Sphingolipid II
- Mito FAS & Lipoic
- Mito LipoPolSach
- Mito Phospholipid
- Trafficking
- Cutin I
- Cutin II
- Suberin I
- Suberin II
- Suberin III
- Oxylipin I
- Oxylipin II
- Signaling
-
Enzyme/Protein
Summary -
Loci
Summary -
Structures &
Schemas -
Lipid methods
& composition - Mutants
- Downloads
- About
- Comments


