|
|||||||||||||

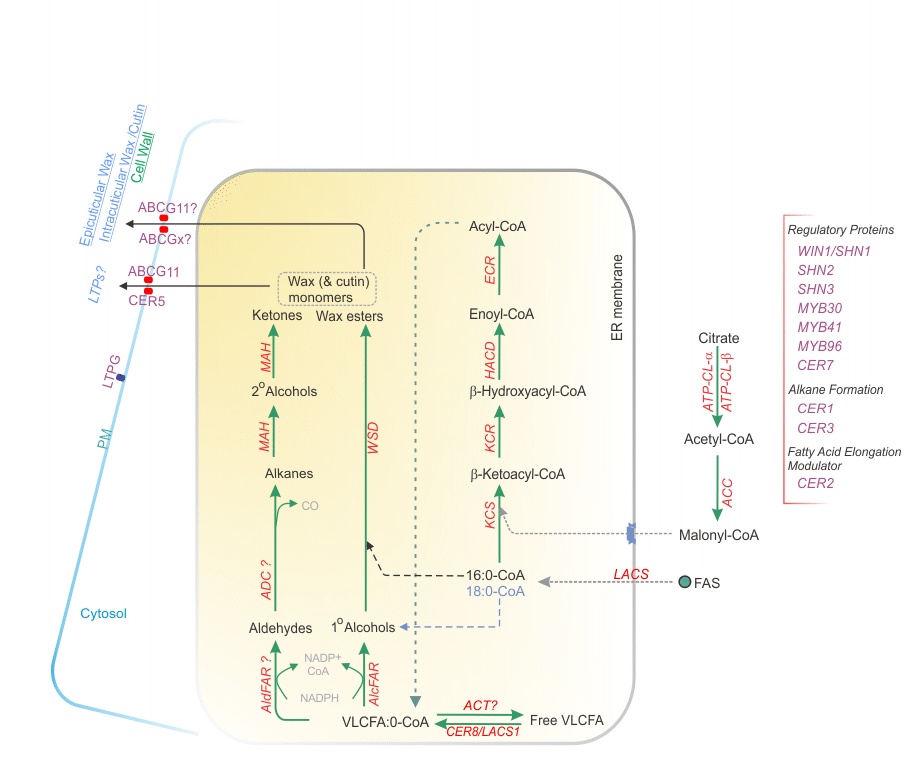
Legend: Pathways for the formation in epidermal cells of very-long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs (VLCFAs) and cuticular waxes. Analogous FA elongation pathways occur in all cells to produce VLCFA for sphingolipids, and in seeds for elongation of 18:1 to 20:1 and 22:1. Saturated C16 and C18 fatty acids, produced in the plastid (FAS), are esterifed to coenzyme A (CoA) by LACS. 16:0- and 18:0-CoA esters are elongated by reiteratively adding a two carbon unit to the carboxy terminal to generate VLCFA wax precursors between 20 and 34 carbons in length. The endoplasmic reticulum(ER)-associated fatty acid elongase consists of four enzymatic activities (KCS, KCR, HACD, and ECR) that work sequentially to elongate the fully saturated acyl-CoA chains. Once the VLCFAs are synthesized, they are converted to cuticular waxes by the coordinated activities of a number of enzymes. A proportion of the elongated acyl-CoAs are hydrolyzed by a thioesterase to release free fatty acids. Conversely, free VLCFAs can be re-activated into CoA esters by LACS1. However, most of the elongated fatty acyl-CoAs enter one of two wax biosynthetic pathways: an alkane-forming pathway (also known as the decarbonylation pathway) that produces aldehydes, alkanes, secondary alcohols and ketones, and a primary alcohol forming pathway (also known as the acyl reduction pathway) that produces primary alcohols and wax esters. The waxes are transported to the plasma membrane (PM) by an unknown mechanism and transport across the PM is facilitated by ABC transporters (CER5 and ABCG). Lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) may be involved in transport of waxes across the cell wall in order to reach the final destination at the cuticle.
Abbreviations: ATP-CL-α(β), ATP citrate lyase α(β) subunit; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase (Cytosolic; Homomeric ); MCD, malonyl-CoA decarboxylase; LACS, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; KCS, ketoacyl-CoA synthase; KCR, ketoacyl-CoA reductase; HACD, hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrase; ECR, enoyl-CoA reductase; THS, acyl-CoA thioesterase; AlcFAR, alcohol-forming fatty acyl-CoA reductase; WS, wax synthase; WSD, bifunctional wax ester synthase / diacylglycerol acyltransferase; AldFAR, aldehyde-forming fatty acyl-CoA reductase; ADC, aldehyde decarbonylase; MAH, midchain alkane hydroxylase; MAO, midchain alkanol oxidase; ABCG, ATP-binding cassette transporter G subfamily; CER5, ECERIFERUM 5; LTP, lipid tTransfer protein; LTPG, GPI-anchored lipid transfer protein; VLCFA, very long-chain fatty acid. Fatty Acid Elongation & Wax Biosynthesis
|
|||||||||||||
-
Home &
Pathways- Home
- Fatty Acid Synth
- Plast FAE & Desat
- Prok Gal/Sulpho I
- Prok Gal/Sulpho II
- Euk Gal/Sulpho
- TAG Synthesis
- Euk Phospholipid
- TAG Degradation
- FA Elong & Wax
- Sphingolipid I
- Sphingolipid II
- Mito FAS & Lipoic
- Mito LipoPolSach
- Mito Phospholipid
- Trafficking
- Cutin I
- Cutin II
- Suberin I
- Suberin II
- Suberin III
- Oxylipin I
- Oxylipin II
- Signaling
-
Enzyme/Protein
Summary -
Loci
Summary -
Structures &
Schemas -
Lipid methods
& composition - Mutants
- Downloads
- About
- Comments


